
Machine shipments reflect continued Chinese domination
The 2015 survey by ITMF was compiled in cooperation with over 140 textile machinery manufacturers.

25th May 2016
Knitting Industry
|
Zürich
According to the latest International Textile Machinery Shipment Statistics (ITMSS) report from the International Textile Manufacturers Federation (ITMF), shipments in some of the textile machinery segments experienced declines in 2015. Deliveries of new short-staple spindles for example fell by nearly 8% from 2014 to 2015. Shipped long-staple spindles and open-end rotors meanwhile decreased by 61% and 6%, respectively. The number of shipped draw-texturing spindles fell by 26% and shipments for new circular knitting machines by 6% year-on-year. By contrast, deliveries of shuttle-less looms increased by 14% in 2015 and shipments of flat-knitting machines rose by a massive 52%.
The report covers six segments of textile machinery, namely spinning, draw-texturing, weaving, large diameter circular knitting, flat knitting and finishing. The 2015 survey was compiled in cooperation with over 140 textile machinery manufacturers, representing a comprehensive measure of world production. According to the ITMF, this number does not include the numerous Chinese companies that are represented by the so called ‘District’. Therefore, the amount of participating companies is likely to be around 200.
Global shipments of large circular knitting machines fell by 6% to a level of 26,700 units in 2015. Also for this category, Asia is the world’s leading investor. 88% of all circular knitting machines were shipped to Asia in 2015. With 53% of worldwide deliveries China is the single largest investor. India and Bangladesh rank second and third with 6,500 and 3,100 units, respectively.
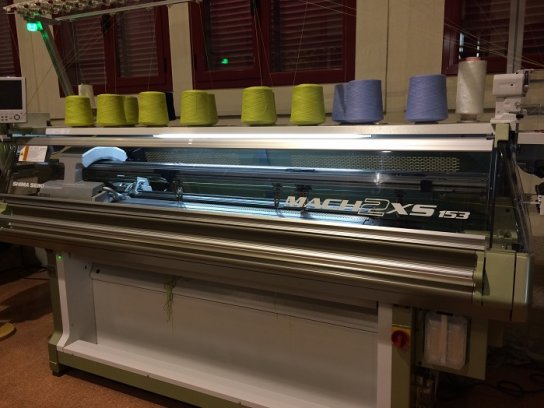
2015 was a very good year for the segment of electronic flat knitting machines as global shipments grew by 52% to 70,100 machines, the highest level since 2011. Not surprisingly, Asia received the highest share of shipments (93%). China remained the world’s largest investor for flat knitting machines in 2015 with Chinese investments increasing from 19,000 units to 35,500 units.
Shipments of new short-staple spindles fell by nearly 8% year-on-year in 2015, the second decrease in a row. The level of short staple spindles declined to about 9 million spindles, the lowest level since 2009. Most of the new short staple spindles (92%) were shipped to Asia, whereby shipments fell by 7% year-on-year. Thereby China, the world’s largest investor of short-staple spindles, experienced a decline of 26%, whereas deliveries to Bangladesh, Indonesia and Vietnam rose by 97%, 4% and 31%, respectively. All of the five largest investors for short-staple spindles in 2015 originate from Asia. Including China these are India, Vietnam, Bangladesh and Indonesia.
Global shipments of long-staple (wool) spindles decreased sharply by 61% from around 138,000 in 2014 to nearly 54,000 in 2015. Deliveries to Turkey, one of the main investors of long-staple spindles in the last few years, fell by 83% from 67,000 in 2014 to over 11,000 spindles in 2015. The majority of long-staple spindles (58%) were shipped to Asia. Nearly 41% of long-staple spindles had Europe as destination. In 2015, Iran was the largest investor with 14,200 spindles, followed by China with over 13,000 spindles.
Shipments of open-end rotors fell by 6% to a level over 383,000 rotors in 2015. About 81% of worldwide shipments of open-end rotors were destined for Asia. Thereby, deliveries to Asia increased moderately by over 2% to nearly 312,000 rotors. In contrast, regions such as North America and Western Europe recorded annual percentage declines of 47% and 60%, respectively. Shipments to China, the world’s largest investor of open-end rotors, increased massively by around 66% in 2015. The world’s second and third largest investors in 2015 were India and the USA.
Global shipments of single heater draw-texturing spindles (mainly used for polyamide filaments) fell by nearly 82% from over 6,500 in 2014 to nearly 1,200 in 2015. With 65% Asia is the region where most of the single heater draw-texturing spindles were shipped to, followed by Eastern Europe with 32% and South America with nearly 3%.
In the segment of double heater draw-texturing spindles (mainly used for polyester filaments) the downward trend continued and global shipments fell by 25% on an annual basis to over 322,000 spindles. Asia’s share of worldwide shipments amounted to close to 81%. Thereby, China remained the largest investor accounting for 57% of global shipments.
In 2015, worldwide shipments of shuttle-less looms increased by 14% to nearly 82,000 units. Thereby, shipments of water-jet and rapier/projectile shuttle-less looms increased by 24% to nearly 30,000 looms and by 17% to close to 32,000. In contrast, the deliveries of air-jet looms fell by over 1% to a level of nearly 20,000 looms.
Not surprisingly, the main destination of shipments of all shuttle-less looms (air-jet, water-jet and rapier/projectile) in 2015 was Asia with 93% of worldwide deliveries, of which 39% were water-jet looms and 37% rapier/projectile looms. In Europe and North America 75% and 25% of shipments were for rapier/projectile looms, while the share of water-jet looms was only 8% and 2%, respectively.
The 2015 edition of ITMF's International Textile Machinery Shipments Statistics also included for the tenth time data on finishing machinery. However, the questionnaire was revised to present a more accurate picture of shipments in this sector. Therefore, it is not possible to compare this version with previous versions of the finishing machinery statistics, the ITMF reports.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more